Partner: Misterine s.r.o.
Field: Healthcare Industry
 Misterine is a Prague-based pioneering company specializing in innovative AR and VR solutions for diverse industries worldwide. They are expanding their technology capabilities through VR training infrastructure and digitalizing the service industry. Their Misterine Studio & App enables users to effortlessly create, edit, and play AR manuals for a better understanding of complicated manual procedures. They partner with firms focused on digital transformation, leveraging AR’s potential in data visualization to simplify workflows and optimize data transfer.
Misterine is a Prague-based pioneering company specializing in innovative AR and VR solutions for diverse industries worldwide. They are expanding their technology capabilities through VR training infrastructure and digitalizing the service industry. Their Misterine Studio & App enables users to effortlessly create, edit, and play AR manuals for a better understanding of complicated manual procedures. They partner with firms focused on digital transformation, leveraging AR’s potential in data visualization to simplify workflows and optimize data transfer.
Misterine’s AR and VR solutions enable better visualisation and education through immersive 3D experiences. As part of the collaboration, the National Competence Centre in HPC (NCC) leveraged the long-standing expertise of scientists at IT4Innovations National Supercomputing Center to create 3D tissue models for visualisation using supercomputers. Such tissue models can be used, for example, for AR training from medical image data. Incorporating the new features into Misterine’s existing workflow and ensuring seamless integration with NCC’s workflow while maintaining data integrity presented a major challenge. The main objective is to describe a possible integration of the workflows, optimize visual fidelity and performance by adding suitable materials to the 3D mesh or volume, add the possibility of cutting the created models, and reduce the complexity of geometry topology to accommodate AR and VR devices.
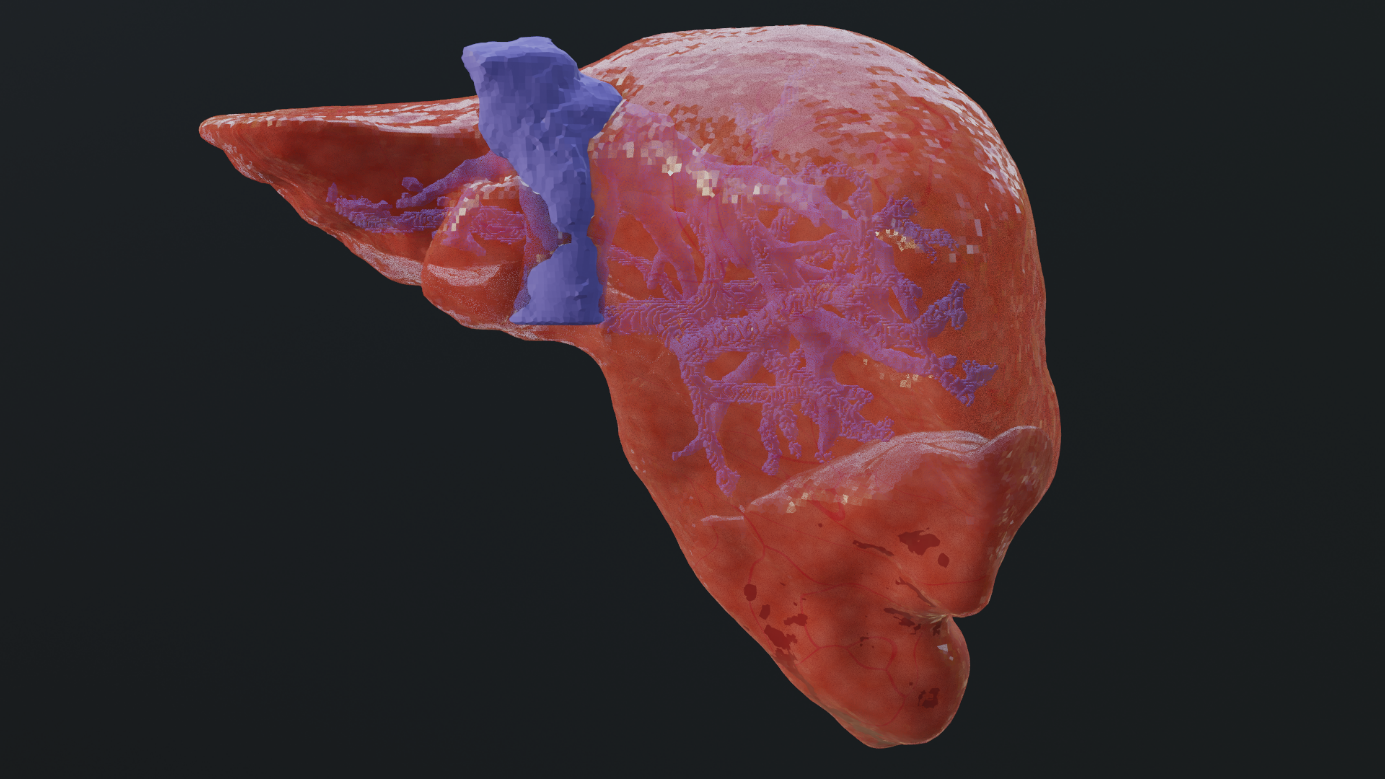
NCC has offered methods to enhance Misterine Studio’s software capabilities to showcase medical tissues in AR and enable workflow execution from the command line. IT4Innovations’s supercomputer processes the data and utilizes deep learning AI models to generate 3D tissue models through remote AI inference. NCC provided solutions for slicing models in a general direction, allowing detailed visualization of the internal structure with realistic textures. Mesh cutting can be achieved with selection tools and logical operations, while volume cutting can be performed using the VTK library or manipulated with mask arrays.
The National Competence Centre in HPC has provided a way to achieve seamless medium-resolution tileable textures and suitable procedural materials for both mesh and volume formats, designed for medical imaging data, ensuring realistic rendering within AR and VR environments. In this case, methods for geometry reduction, including decimation, re-meshing, and signed distance functions (SDFs), have also been used to accurately handle the 3D mesh topology and optimise performance.
Martin Klíma, CTO of Misterine s.r.o.
“The current Misterine workflow lacks support for 3D models from medical imaging. The new methods will help enhance Misterine software capabilities, enabling the showcasing of medical tissues in augmented reality (AR) and facilitating automatic workflow creation and execution from the command line. This, in turn, will enable users to be trained in utilizing AR for medical image data exploration. The visualization can provide valuable insights for medical professionals and researchers, enabling them to study and analyze the tissue more precisely. It will enhance the overall quality and usefulness of Misterine Studio’s software for medical imaging applications.
Using supercomputers, it has been possible to reduce the time of AI model training from computed tomography (CT) datasets. This will help Misterine with advanced data processing capabilities with deep learning. The solutions will also help in optimizing the workflows, reducing the complexity, and realistic rendering using AR and VR devices.”

